Medicare is a vital source of healthcare coverage for millions of Americans, including those in need of durable medical equipment (DME). However, navigating the complex Medicare guidelines for DME billing can be a challenging task for healthcare providers. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key aspects of Medicare guidelines for DME billing, helping providers gain a solid understanding of the requirements, documentation, coding, and reimbursement processes involved.
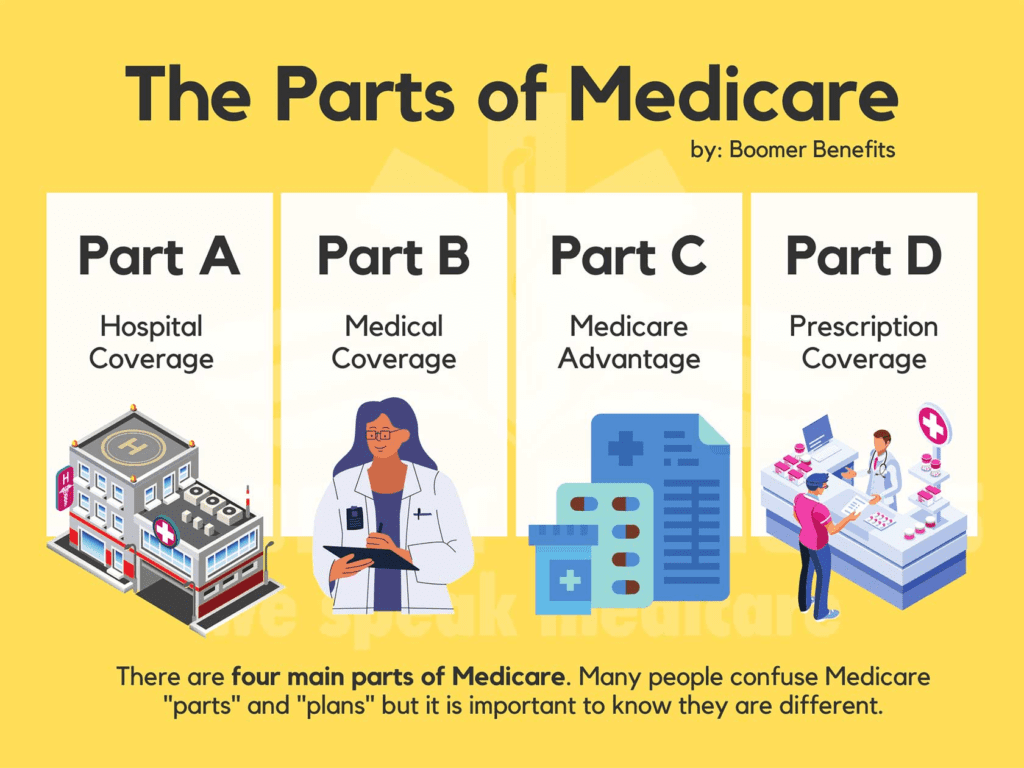
Overview of Medicare DME Coverage:
Medicare Part B coverage for DME: Medicare Part B is a component of Original Medicare that covers medically necessary services and supplies, including DME. We will explore the key features and benefits of Medicare Part B coverage for DME, including the types of DME items covered and the specific conditions and criteria for coverage.
Eligibility criteria for Medicare DME coverage: To be eligible for Medicare DME coverage, beneficiaries must meet certain criteria. We will discuss the eligibility requirements, including age, disability status, enrollment in Medicare Part B, and the role of medical necessity in determining coverage. Understanding these criteria will help providers determine if their patients are eligible for Medicare DME coverage.
Differentiating between covered and non-covered DME items: Medicare has specific guidelines on what DME items are covered and what is considered non-covered. We will provide an extensive list of commonly covered DME items, such as wheelchairs, walkers, oxygen equipment, and more. Additionally, we will discuss non-covered DME items, including items that are not deemed medically necessary or are specifically excluded by Medicare.
Medicare Documentation Requirements:
Proper documentation is crucial when billing Medicare for durable medical equipment (DME) services. Medicare has specific documentation requirements that healthcare providers and suppliers must adhere to in order to ensure accurate reimbursement and compliance.
1. Detailed overview of the necessary documentation for DME claims:
Prescription and Order Documentation:
- Explain the requirement for a valid prescription or order from an authorized healthcare professional for Medicare-covered DME items.
- Discuss the specific information that should be included in the prescription or order, such as the patient’s name, diagnosis, specific DME item prescribed, quantity, and duration of use.
Detailed Item Description and Cost Information:
- Highlight the need to provide a detailed description of the DME item, including its make, model, and any necessary accessories or supplies.
- Discuss the importance of including the cost information, such as the purchase or rental price of the equipment, to support the reimbursement claim.
Proof of Medical Necessity:
- Explain the requirement to demonstrate the medical necessity of the DME item through comprehensive clinical documentation.
- Discuss the need to include relevant medical records, such as physician progress notes, test results, and therapy reports, to support the medical necessity claim.
2. Importance of accurate and comprehensive documentation:
Ensuring Reimbursement:
- Emphasize that accurate and comprehensive documentation is crucial for receiving proper reimbursement from Medicare.
- Explain how documentation serves as evidence to justify the medical necessity of the DME item and supports the claim for reimbursement.
Compliance with Medicare Guidelines:
- Discuss how accurate documentation ensures compliance with Medicare’s rules and regulations.
- Highlight that adherence to documentation requirements minimizes the risk of audit, claim denial, or potential penalties.
3. Common documentation pitfalls to avoid:
Insufficient or Incomplete Documentation:
- Explain the risks associated with inadequate documentation, such as claim denials or delays in reimbursement.
- Provide examples of common pitfalls, such as missing or incomplete information, vague descriptions, or lack of supporting medical records.
Lack of Specificity in Medical Necessity:
- Highlight the importance of clearly articulating the medical necessity of the DME item.
- Encourage healthcare providers to provide detailed explanations and supporting evidence to avoid claim denials due to insufficient medical necessity documentation.
Failure to Keep Updated Documentation:
- Emphasize the need for up-to-date documentation that reflects the current medical condition and ongoing need for the DME item.
- Encourage regular review and updates to ensure accuracy and compliance with Medicare guidelines.
By understanding the necessary documentation, recognizing the importance of accurate and comprehensive records, and avoiding common pitfalls, healthcare providers can ensure compliance, expedite reimbursement, and provide quality DME services to Medicare beneficiaries.
DME Coding and Billing Guidelines:
1. Introduction to HCPCS (Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System) codes:
The Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) is a standardized coding system used in the United States to describe medical procedures, services, supplies, and equipment provided to patients. It consists of two levels: Level I codes, which are based on Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes developed by the American Medical Association (AMA), and Level II codes, which are specific to healthcare products, supplies, and services not included in the CPT codes.
2. Explanation of DME-specific HCPCS codes and modifiers:
DME-specific HCPCS codes play a crucial role in accurately identifying and billing for durable medical equipment (DME) items and services. These codes provide a standardized way to describe the specific DME items being provided to patients. They help in ensuring proper reimbursement and facilitating claims processing.
DME-specific HCPCS codes include a wide range of equipment and supplies, such as wheelchairs, hospital beds, oxygen equipment, walkers, and more. Each DME item is assigned a specific HCPCS code that accurately represents the item and its attributes.
In addition to HCPCS codes, modifiers are used to provide additional information about the DME item or service. Modifiers can indicate factors such as the rental versus purchase of equipment, the condition of the equipment, and any additional services or supplies associated with the DME item. Modifiers help to further specify the details of the DME item being billed, ensuring accurate coding and billing.
Check out our Tips for accurate coding and billing to ensure proper reimbursement.7
Medicare DME Fee Schedule:
1. Understanding the Medicare DME fee schedule and its impact on reimbursement:
The Medicare Durable Medical Equipment (DME) fee schedule is a pricing system used by Medicare to determine the reimbursement rates for DME items and services. It sets the maximum allowable amount that Medicare will pay for specific DME items based on factors such as the item’s cost, geographic location, and other relevant considerations.
The fee schedule plays a crucial role in determining the reimbursement amounts for DME claims. Providers must understand how the fee schedule works and how it impacts their reimbursement rates. By knowing the fee schedule rates, providers can accurately calculate their expected reimbursement and ensure that their billing aligns with the Medicare guidelines.
2. Updates and changes to the fee schedule:
The Medicare DME fee schedule is subject to periodic updates and changes. It is essential for providers to stay informed about any revisions to the fee schedule, as these updates can affect reimbursement rates and billing practices. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) releases annual updates, which include changes to the fee schedule, new codes, modifiers, and reimbursement policies.
Providers should regularly review the updates and stay updated on any changes that may impact their DME billing. This helps ensure compliance with the latest guidelines and maximize reimbursement rates for their services.
Know more about the Strategies for maximizing reimbursement within the fee schedule.
Medical Necessity and Coverage Criteria:
Explaining the concept of medical necessity in Medicare DME billing:
Medical necessity is a crucial concept in Medicare DME billing, as it determines whether a particular DME item is eligible for coverage and reimbursement. Medicare requires that DME items meet the criteria of medical necessity, meaning they are deemed reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of a medical condition.
To establish medical necessity, the healthcare provider must demonstrate through proper documentation that the DME item is required to diagnose, monitor, or treat the patient’s medical condition. This documentation should include clinical indications, relevant medical history, examination findings, and any other supporting information that justifies the need for the DME item.
Coverage criteria for different types of DME items:
Medicare has specific coverage criteria for different types of DME items based on the item’s intended use and its classification under the Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes. Here are some examples of coverage criteria for commonly used DME items:
Mobility devices: Medicare covers mobility devices such as wheelchairs, power-operated vehicles (scooters), and walkers if the patient has a mobility impairment that significantly impairs their ability to participate in daily activities within the home.
Oxygen equipment: Medicare covers oxygen equipment and supplies for patients with severe lung diseases or hypoxemia, where supplemental oxygen is medically necessary to improve or maintain their condition.
Orthotic devices: Medicare covers orthotic devices like braces and supports when they are medically necessary for the proper alignment, support, or protection of a specific body part due to an injury, deformity, or medical condition.
Prosthetic devices: Medicare covers prosthetic devices such as artificial limbs or limbs replacement when they are necessary to restore or improve the functioning of a body part that is permanently missing or nonfunctional.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) machines: Medicare covers CPAP machines for patients with diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea, where the use of the machine is medically necessary to treat the condition and improve breathing during sleep.
It’s important for healthcare providers to understand the specific coverage criteria for each type of DME item to ensure proper billing and reimbursement. Adhering to the coverage criteria helps avoid claim denials and ensures that patients receive the necessary DME items for their medical conditions.
By explaining the concept of medical necessity and providing an understanding of the coverage criteria for different types of DME items, healthcare providers can navigate Medicare DME billing more effectively and ensure appropriate coverage and reimbursement for their patients’ needs.
Learn the tips for meeting medical necessity requirements to ensure reimbursement.
Claims Submission and Reimbursement Process:
Step-by-step guide to claims submission for Medicare DME billing:
- Gather necessary documentation.
- Verify patient eligibility.
- Assign accurate HCPCS codes.
- Complete the claim form accurately.
- Submit the claim to the MAC.
Explanation of the Medicare claims review and adjudication process:
- Initial claim review for completeness and validity.
- Claims processing, eligibility verification, and coding checks.
- Thorough review for compliance with coverage criteria and regulations.
- Claim determination for approval or denial.
Timelines and important considerations for reimbursement:
- Timely filing within specified deadlines.
- Maintain comprehensive documentation.
- Understand the appeals process for denials.
- Stay updated on reimbursement changes and policies.
By following the step-by-step guide, understanding the claims process, and considering reimbursement considerations, providers can optimize their Medicare DME billing and reimbursement outcomes.
Understanding the Medicare guidelines for DME billing is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure proper reimbursement, compliance, and efficient revenue cycle management. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the coverage criteria, documentation requirements, coding guidelines, and reimbursement processes, providers can optimize their DME billing practices and deliver quality care to Medicare beneficiaries.


